5 Components of Geoanalytics guide, Geographic information system data tips, GPS and satellite photos
5 Components of Geoanalytics
5 Mar 2021
Geoanalytics collect, display, and manipulate geographic information system data like imagery, GPS, satellite photos, and more. By using coordinates, addresses, and postal codes to create geographical models including maps, graphs, statistics, and histograms, geoanalytic tools can be extremely helpful. These models are useful data visualization tools that help users better understand large datasets. Geoanalytics tools give insights into historical changes, current shifts, and future changes.
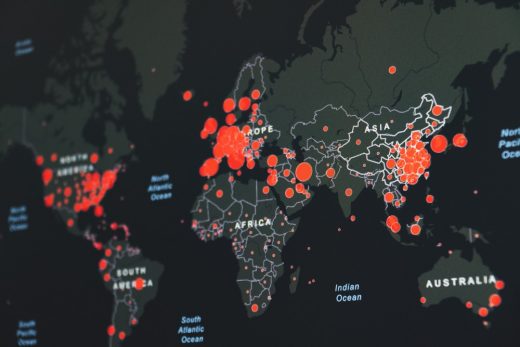
Giving more information about the timing and location provides context to datasets. Maps make it easier to notice patterns in big datasets such as proximity, affiliation, and distance. Businesses can see real-time insights of geo-referenced data by incorporating the Internet of things (IoT), location sensors, social media, and mobile devices.
Geoanalytics also helps businesses make better decisions by helping them understand the complexities of relationships in data in a geographical context and how to accurately interpret them. Businesses need to understand consumer behavior and demands in all markets to meet customer expectations. Geoanalytics track user engagements based on regions or areas on web applications and mobile services.
There are several use cases for geoanalytics, but to get the full benefits of geoanalytics tools, businesses need to think beyond maps. A solution that allows for automated map creation with real-time geocoding, multiple data layers, and GIS data is essential for unlocking the benefits of geoanalytics.
The first step in Google Maps advertising is to create a GMB account. As soon as the account is created, you ought to optimize its core elements. Once this is achieved, you should request verification via a postcard. This procedure can take numerous weeks. Whilst you obtain your verification code, you may use it to affirm your commercial enterprise profile. It will take two to a few weeks for the code to reach. Googelecom
1. Interactive Mapping
Businesses can use interactive maps to overlay them with different data visualizations. Real-time location lookup functions increase productivity while improving the understanding of location information and how it relates to data. Interactive mapping eliminates the need for mapping separate datasets, overhead, and maintenance costs.
2. Geospatial Insights
Geoanalytics provide real-time insights into patterns faster than traditional analytics. Businesses can use immersive visualizations to analyze location relationships, existing data, and their applications. These insights help businesses better understand the full story of their data.
3. Geographic Search and Clustering
Businesses can look up locations on-demand to populate analyses, update dashboards, maps, and other data visualizations. Geographic searches allow businesses to analyze datasets by city, zip code, coordinates, and more. It’s easy to identify clusters of data points or events with clustering. Observing clusters of high or low values can impact business decisions.
4. Formatting and Annotating
Geoanalytics feature formatting tools that allow users to mark up data with colors, lines, and shapes to better understand information. This, in turn, helps users to visualize datasets and aggregate points, and make better business decisions as a result.
5. Layers and Target Highlighting
The different views of datasets produced by visual mapping help users analyze datasets on a layered map. The different feature layers can be set over heatmaps, chart, bubble, geodata, and other types of layers. You can also select specific layers to further investigate with different variables to find locations and better understand patterns.
Why do geoanalytics matter to businesses?
Geoanalytics help businesses discover valuable insights and opportunities for scalability. All business applications contain geographic data from GIS that overlap location details on maps that help visualize information to pinpoint market areas using patterns, colors, or shades. The amount of big data collected by marketers helps them better meet market demands. Location analytics allow businesses to identify which markets to expand to and where to build customer relationships in use proximity to competitors.
Location analytics determine how and where businesses can reap the maximum benefits. Understanding where to expand business operations allows businesses to make accurate improvements and provide cost-effective solutions. Marketers can identify new market opportunities and determine which markets are underperforming and either change tactics or drop the markets.
When businesses can see what’s going on in real-time and see location-based events, they can take decisive actions. Businesses can also resolve issues on the fly by relying on geographic boundaries. The ability to visualize routing scenarios helps businesses clearly define critical information for logistics, workflow, and supply chain management.
Comments on this guide to 5 Components of Geoanalytics guide – Geographic information system data info article are welcome.
Building Articles
Residential Architecture Design
Green Massage Healthcare Center, INFINITUS Mall, Shanghai, China
Architecture: Vermilion Zhou Design Group
Green Massage Healthcare Center
Comments / photos for the 5 Components of Geoanalytics guide, Geographic information system data advice page welcome