Eco Bridge Design Competition Seoul, Korean Architecture Contest, Building Design
Eco Bridge Design Competition in Seoul
South Korea Road Crossing: Yangjaegogae Architecture design by KILD architects
23 Jun 2017
Yangjaegogae Eco Bridge Design Competition in Seoul by KILD
Architects: KILD – Ksnelashvili . Išora . Lozuraitytė . Daunys
Location: Seoul, Korea
1st prize winner at YANGJAEGOGAE ECO BRIDGE DESIGN COMPETITION
Design concept
‘SLOPE-WALK’
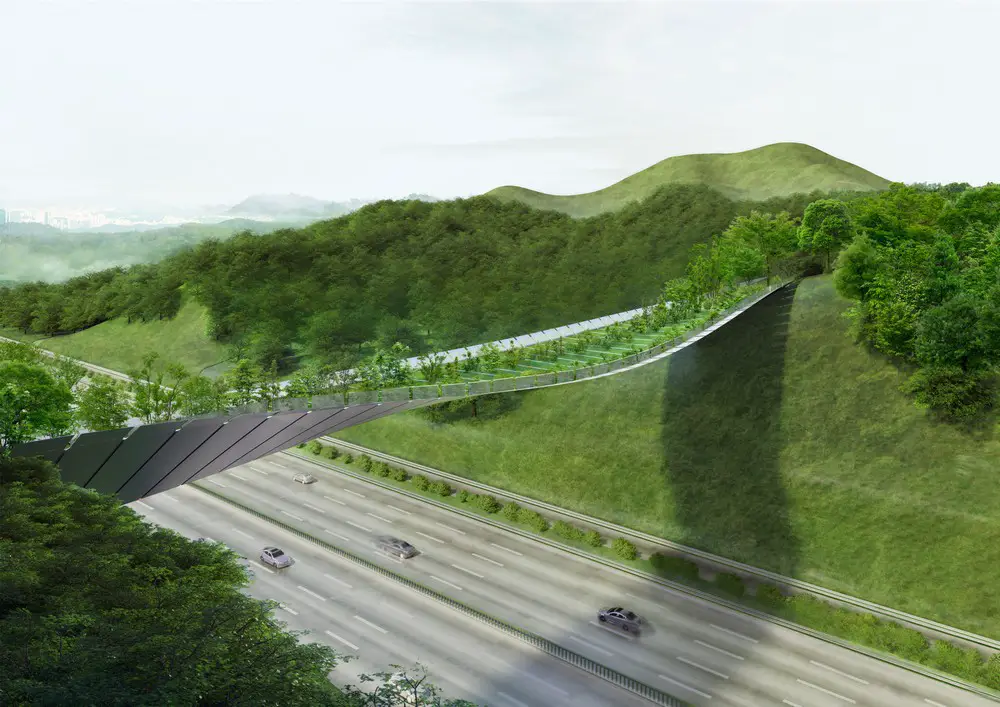
The Eco Bridge proposal is based on a simple and pure concept: to recreate the link that once existed in the current situation of the infrastructural void with a spatial structure that would be atmospherically reminiscent to a pictorial passage through the southern slopes of the two discontinued mountain peaks of Mt. Umyeon and Maljukgeori Parks.
The proposal is inspired by the naturally green integrity of mountain peaks – the inherent part of Mt. Umyeon and Maljukgeori Parks and the landscape experience of the accompanying side slope paths.
Eco-Bridge birds eye view:
The landscape of the bridge is referential to the natural, informal, simplistic and unforced nature of Korean gardens. The architectural language of the structure of the intervention is tender to the rhythmic nature of the traditional Korean garden pavilions traditionally used to invite for the enjoyment of the surrounding garden sceneries.
view from the highway:
The path for human passage
Continuation of the existing mountain slope surface with the help of bridge that is extending the spatial experience of walking the path near a slope.
Sided on the two discontinued south slopes, the one-sided link as space is therefore less windy and mostly sunlit, which follows a naturally dualistic spatial experience of walking on the side of the mountain – one of the panoramas and one of the close-ups of the hillside landscape.
Only the midpoint of the bridge stays open toward the spectacular panoramic view of Seoul on the north.
view walking on the bridge:
A landscape for animal transit
Mountain peak habitat formation on the both access zones of the habitat bridge by keeping upper parts of the two linked mountain peaks uninterrupted by people for the priority of the animals and the continuation of this elevated privilege with the help of the structurally formed slope on the bridge part of the new Eco-Structure.
Dual structure
The two intended environments suggest a structural concept:
Arch bridge (central core) forming a straight human path + an integration of suspended bridge structure on its side that is forming a gently undulating slope between the two mountain peaks (slope) for the animals.
The structure in positioned in the altitude that is convenient to separate the human and the animal realms in the elevation (upper part serves for the nature and the lower part for the people)
concept diagrams / contexts:
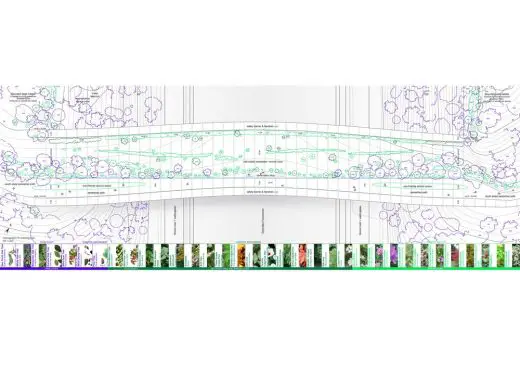
Landscape plan
The key spatial element is a consistent slope that is gradually lowered in the midpoint of the bridge. The layers of trees, semi-trees, shrubs and smaller plants are composed with a principle of gradual entropy starting from the slopes of the mountains towards the midpoint of the bridge.
The chosen gradual zoning of the planting reaches for diversification in time, stabilized maintenance and enhanced biodiversity.
Larger trees are positioned on the access and gradually get smaller. This is supported by a larger soil pots and consequently smaller pots gradually shifting towards the midpoint of the bridge, following the general geometry and proportions of the bearing structures.
The design creates a sequence of varied gradually shifting environments within a cohesive and singular sloped landscape.
Blurred boundaries between the walkway and the plantings are positioned highlighting a notable natural boundary between human walking area and animal transit zone with a diverse undisrupted shrub layer.
The naturalistic dirt path becomes a linear and constant side of the slope and suggests a simple, wild, quiet and slowed-down experience of the bridge passage.
Zones for eco-friendly activity are positioned on the wider part of the path nearby the larger plantings.
concept diagram / slopewalk:
A Soils and ground surface
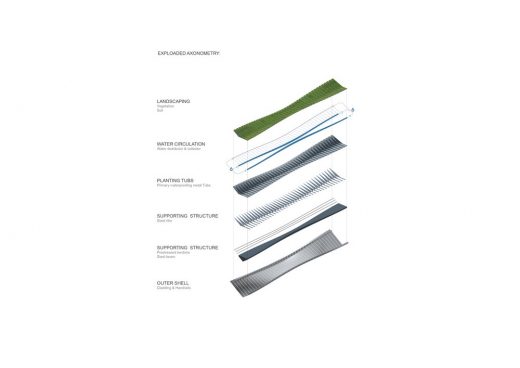
Modulation of the structure incorporates a segmented assembly of structural planting tubs that are filled with the necessary layers of the soil and vegetation and are supported by technological layers (see: maintenance). All combined in a singular system of self-sufficient structured and technologically advanced naturalistic landscape as a balanced micro-ecosystem.
B Vegetation
Plant communities build on the sloping landscape are designed to produce a primarily wild, native, resilient and low-maintenance landscape with great diversity, seasonal change, and height, color variation.
Food plants, trees bushes, and grassland species are set to improve the linear transit logic of the link, support the natural divisions between human and animal realms, and sets a linear zoning of the landscape, that multiplies the number of scenarios how to cross it. The plantation sets are laid down in a dashed linear sequence that enhances every interval of the animal passage with a diverse mix of flora and maximizes the usage of recommended plant species.
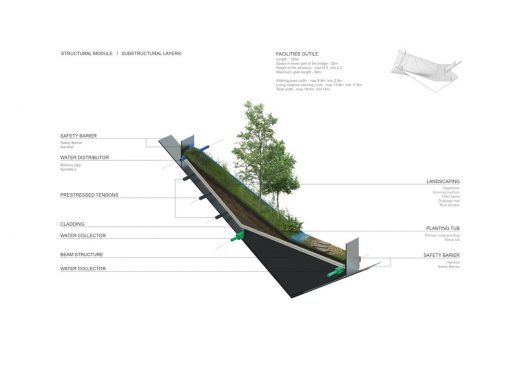
section / structural module and substructural layers:
Traffic line plan
A -Traffic line plan
The human path links the existing ones with the most proximate straight passage (in the alt. 64th), continuing the character of the slope path on the bridge and the access zones. Slope condition helps to positions the human and animal path in naturally different levels, keeping the animal in a safer and secured upper position (Alt. 70th and 75th with an inclination toward the path). The natural character of the division is intensified with a proposed Hilltop Habitat zones for animals only, leaving the human path as its natural boundary.
Water ditch is integrated on the breaking line where the slope meats the dirt path and is serves for the means of migration of reptilians and amphibians.
B – Width of structure
The width of the animal passage gradually spans from 11.5m to 13.8m, and is enhanced both in height as the slope character of the bridge introduces a continuous shift from +6m to +1m and back to a +11m difference in height all through the animal landscape between both entry sides of the bridge.
C – Minimize interruptions
The slope character lets to naturally separate the zones in level, leaving the safer higher zone for animals only. That is being supported by a linear naturally arranged planted boundary. The boundary is additionally equipped with newest information technology, that informs the passengers on the processes of ecosystem and gives a possibility of close-up surveillance of the natural processes without entering the animal zone and is exposed in a discrete and calm way. Zones of ecofriendly activities are outlined on the wider parts of the human path for proximate activities in nature without physical intervention into the animal habitat.
D – Entrance and exit
Entry is maximized with the proposed Hilltop Habitat zones and the introduction of the maximized difference in height between animal and human paths (+6m and +11m). The division is highlighted with the introduced selected plantation. The plantation additionally forms spatial jaws on the entry of bridge that naturally collect the roaming animals in a natural inviting logic.
structural diagram:
Maintenance plan
A Economic
We have selected a type of construction that dates back to origins of bridge building: a sum of an arched beam structure accompanied by a tensile cable (hanging) bridge structures. The structure is designed out of metal that helps to reach its most proximate parameters. The construction methodology is specified in the implementation phasing chapter (see: boards Implementation phasing). The bridge is planned as a self-efficient closed circuit environment, that is additionally powered from the central electricity system.
B Safety
Structural safety barrier of two layers (min 2.3m wide zone) are introduced on both sides of the bridge. The safety barriers on the side of the animals is additionally supported by a formation of the dense row of bushes.
The slope of the bridge reduces the wind, and half closed spatial condition on the bridge is maximally lit and warm as it is facing south.
All plant and construction materials would be brought and remover by the cable crane, leaving a minimal impact on the environment.
Each stage of activity will be risk assessed in detail. Construction methodologies that maintain site safety will be established as an integral part of the development design.
C Management
Structural modules feature a segmented maintenance of the soil and vegetation.
Each module serves a ‘pot’ for a complex layering of technological and natural elements, and is supported by integrated drainage and irrigation system, that is using collected rainwater from the planned water reservoir near the bridge.
The lower part of the structure is insulated and waterproofed to keep a stable and inert regime of the ecosystem during the seasons. An integrated electricity warming system is integrated in the lower parts of the soil – technical layers, to keep a stable temperature during the critical moments of the winter season.
Service terrace together with a water reservoir is designed in the amenities of the bridge and is linked with a separate route to the drop of point near the road on the lower terrace of the territory.
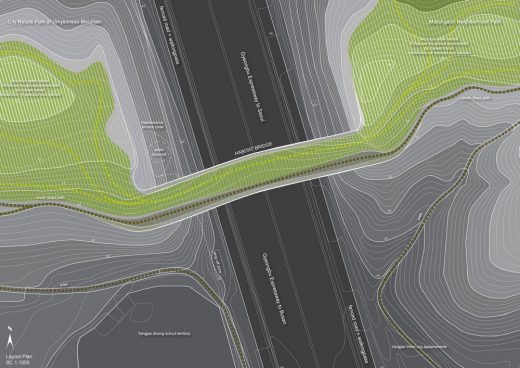
site plan:
Structure plan
A Location and the size of the structure
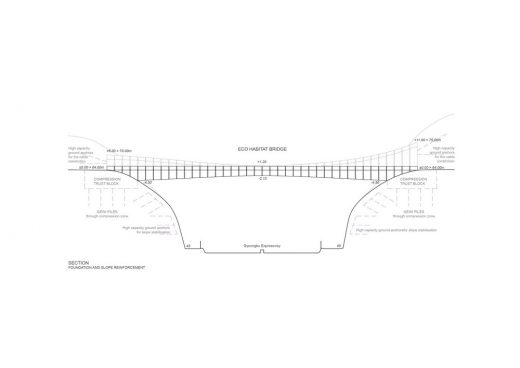
The bridge in positioned in the altitude that is convenient to separate the human and the animal realms in the elevation. The human path level connects 64th (+-0.00) altitude of the mountains on both sides of the expressway in a linear order.
The slope formed on the bridge bends alongside the curve of the hanging steel cable the structure. It connects the 70th (+6.00) and 75th (+11.00) altitudes of the siding mountains, bending with a natural curvature until the 65th (+1.00) altitude in the middle of the bridge.
The lower part of the structure is 29m above the surface of the expressway.
In plan the linear part of the structure is positioned on the southern side of both slopes, serving as an optimal pedestrian connection and as a natural boundary of the newly formed mountain peak habitat zones that are recommended to be kept as the animal priority zones without human traffic.
The altitudes of the slope of the bridge in plan naturally merge with the mountain peak topography and help to create an upper level zone for animals that maximizes natural distinction of animal and human traffic zones in levels, avoiding any unnatural barriers for the division.
B Structure design
Dual structure: Arch bridge (central core) forming a straight human path + an integration of suspended bridge structure on its side that is forming a gently undulating slope between the two mountain peaks (slope) for the animals.
From the top views, the bridge gently blends with the topography of the surrounding curvy landscapes. From far away the metal clad bridge forms a monumental sign highlighting the superimposition of the mountains and the expressway. The duality between the top and down exposes both the void of the absent landscape and continuity of the landscape above.
The landscape of the bridge is framed by metal safety barrier & handrails. The same materiality wraps the lower part of the bridge, forming a prominent and distinct boundary between the natural scenery of the Eco Bridge and infrastructural environment of the lower expressway.
The principal stages of construction process are stated out and illustrated in the diagrams in the posters (see: implementation phasing)
C Facilities on the upper part of the program design
The Implementation Phasing is designed to keep uninterrupted expressway traffic, safety, and minimum environmental impact on the site (specified on the boards).
Energy-efficient LED lighting is installed at waist-level and below, illuminating the pathway for safety, while allowing the eye to appreciate the surrounding sceneries and night sky.
landscape / planting plan:
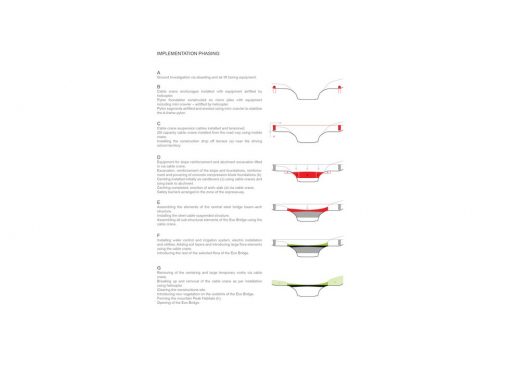
Implementation Phasing:
A
Ground Investigation via abseiling and air lift boring equipment.
B
Cable crane anchorages installed with equipment airlifted by helicopter.
Pylon foundation constructed on micropiles with equipment including mini crawler – airlifted by helicopter.
Pylon segments airlifted and erected using mini–crawler to stabilize the A-frame pylon.
C
Cable crane suspension cables installed and tensioned.
20t capacity cable–crane installed from the roadway using mobile crane.
Installing the construction drop off terrace (a) near the driving school territory.
D
Equipment for slope reinforcement and abutment excavation lifted in via cable crane.
Excavation, reinforcement of the slope and foundations, reinforcement and powering of concrete compression block foundations (b).
Centring installed initially as cantilevers (c) using cable cranes and tying back to abutment.
Centring completed, erection of arch–slab (d) via cable crane.
Safety barriers arranged in the zone of the expressway.
E
Assembling the elements of the central steel bridge beam–arch structure.
Installing the steel cable suspended structure.
Assembling all sub-structural elements of the Eco Bridge using the cable crane.
view from the highway:
F
Installing water control and irrigation system electric installation and utilities.
Adding soil layers and introducing large flora elements using the cable crane.
Introducing the rest of the selected flora of the Eco Bridge.
section:
G
Removing of the centering and large temporary works via cable crane.
Breaking up and removal of the cable crane as per installation using helicopter.
Clearing the constructions site.
Introducing new vegetation on the outskirts of the Eco bridge.
Forming the mountain Peak Habitats (h).
Opening of the Eco Bridge
implementation phasing:
Credits:
Team:
KILD – Ksnelashvili Isora Lozuraityte Daunys
Architects/Authors:
Arch. Ivane Ksnelashvili
Arch. Petras Išora
Arch. Ona Lozuraitytė
Arch. Dominykas Daunys
Stage: Competition 1st prize winner
Type: Habitat Bridge + Landscape
Location: Seoul, South Korea
Client: The Seoul Metropolitan Government
Area: 2600 sqm
Length: 120 m
Project Year: 2017
The team is based in Lithuania, Vilnius.
Eco Bridge Design Competition in Seoul images / information received 230617
Location: Seoul, South Korea, East Asia
South Korea Architecture Designs
Contemporary South Korean Architectural Selection
South Korean Architecture Designs – chronological list
20 Dec 2017
Seoul Creative Play Supporting Facility design by KILD architects

image from architect
Seoul Creative Play Supporting Facility Design Competition by KILD
Blue Line Park, Busan, South Korea
Design: Migliore+Servetto Architects

image courtesy of architecture studio
Blue Line Park in Busan
Comments / photos for the Eco Bridge Design Competition in Seoul page welcome