New vaulted style of floor cuts concrete use, University of Bath Architecture News, Sustainable building design
New vaulted style of floor cuts concrete usage – reducing carbon
19 February 2022
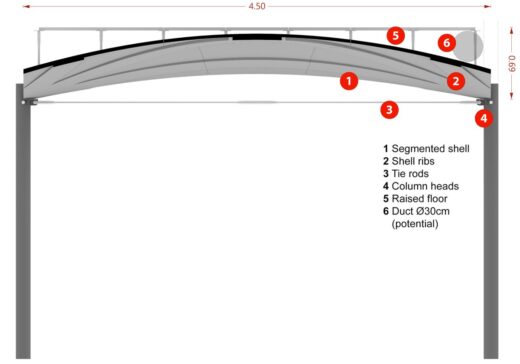
Thin shell concrete floors
Location: University of Bath, southwest England, UK
Changing the shape of floors could cut concrete usage by 75 percent
Swapping solid slab floors for a ‘thin shell’ vaulted alternative could help the construction industry towards its net-zero targets
New vaulted style of floor cuts concrete use
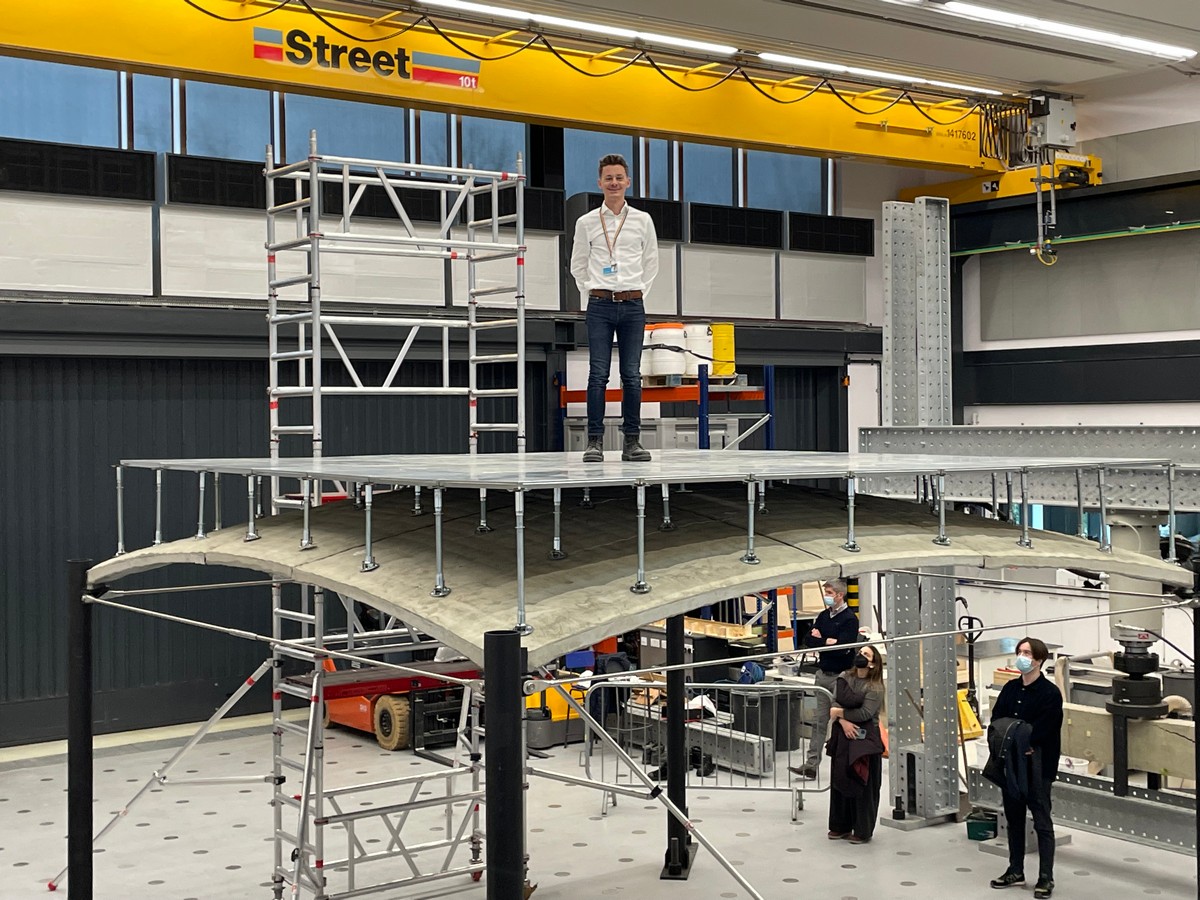
Dr Paul Shepherd of the University of Bath stands on the ACORN project’s thin-shell concrete floor:
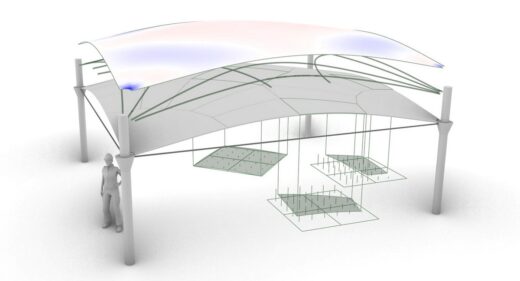
A new vaulted style of floor developed in the UK uses 75% less concrete than a traditional flat slab floor and could help the construction industry reduce its carbon footprint.
An interdisciplinary team of structural engineers, mathematicians and manufacturing experts from the Universities of Bath, Cambridge and Dundee has unveiled a full-scale demonstration of a thin-shell floor, which uses 60% less carbon in its construction than an equivalent flat slab that could carry the same load.
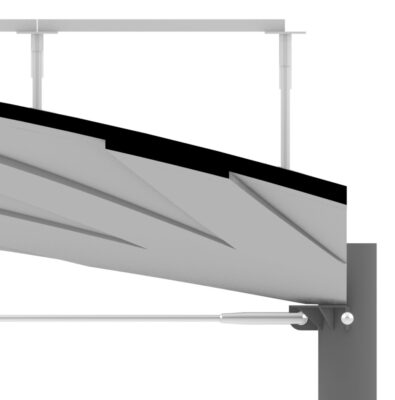
The curved vault-shaped structure is covered by standard raised floor panels to create a level surface.
Created by the UKRI-funded ACORN (Automating Concrete Construction) research project, the innovative vault-shaped floor design takes advantage of concrete’s inherent natural properties and strengths.
The team has demonstrated that the new process could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of our built environment.
Dr Paul Shepherd, a Reader in Bath’s Department of Architecture & Civil Engineering and the Principal Investigator for ACORN, says: “Achieving the net-zero targets recently ratified at the COP26 conference will require significant change by the construction industry, which is responsible for about half of the UK’s total emissions. Since concrete is the world’s most widely consumed material after water, and its production contributes more than 7% of global CO2 emissions, the easiest way for construction to begin its journey to net-zero is to use less concrete.
“That has been the driving force behind this project, which we hope could make a major difference to the impact of construction.”
Innovations in robotics, automated design and off-site fabrication are key
Currently most building floors use thick flat slabs of solid concrete, which are inefficient since they rely on the bending strength of concrete to support loads. Concrete isn’t very good at resisting the tension induced by bending, so these floors also need lots of steel reinforcement. Instead, ACORN’s approach is to use concrete for what it is good at – resisting compression.
By putting the material only where it is needed, and making sure it works in compression, the ACORN design uses far less concrete. The new shape might prove impractical to make using traditional temporary formwork, so the ACORN team has in parallel developed an automated adaptable mould and a robotic concrete spraying system that can be used in an off-site factory setting.
Alongside this new style of fabrication, the team has also developed bespoke software to seamlessly optimise floors for a given building design, and control the automated manufacturing system to produce them.
Since the floor is made off-site, it also needs to be transported to site and then assembled. This brought some exciting challenges for the team, who had to split the large floor into nine transportable pieces and develop a connection system to join the pieces together. However, this also brings some advantages, in terms of reducing time needed on-site for construction.
The ACORN team was also able to incorporate reversible joints, so that the floor can be disassembled and reused elsewhere at the end of the building’s life, promoting a circular economy for the construction industry.
The practicality of this integrated system has just been demonstrated to ACORN’s industry partners, by making a full-scale 4.5m x 4.5m thin-shell building in the NRFIS Laboratory of Cambridge University’s Civil Engineering Department.
Early results suggesting that ACORN’s approach of using material sparingly can already deliver significant carbon savings, with future research likely to lead to even more as processes are optimized. Despite being the first of its kind, each piece took only half an hour to make, and the whole floor took a week to assemble – future commercial versions could be manufactured in dedicated industrial facilities much more quickly, and site erection times much reduced.
Dr Shepherd adds: “After three years of research it is amazing to see the fruits of all our hard work dominating the laboratory and drawing interested looks from all who passed by. It’s not every day you can jump on top of your research! I just hope that one day soon this type of low-carbon automatically manufactured building becomes so widespread that people walk by without noticing.”
Adam Locke, Programme Leader of the Europe Hub Technology & Innovation at Laing O’Rourke, one of the ACORN partners, adds: “The ACORN Demonstrator is a very useful stepping-stone in the progressive pathway to decarbonizing our solutions and compliments very well our own work in this area.”
ACORN has received funding from UK Research and Innovation under the ISCF Transforming Construction programme.
Find out more at the ACORN website: https://automated.construction/
Comments on the New vaulted style of floor cuts concrete usage article are welcome
Previously on e-architect:
University of Bath Posts
15 October 2021
Location: University of Bath, southwest England, UK
‘Wasteful steel-and-glass buildings fuel global climate injustice’

image courtesy of architects practice
Wasteful steel-and-glass buildings fuel global climate injustice
Parallel (of Life and) Architecture – Bath Exhibition
Contemporary reflections on the ideas and impact of Alison and Peter Smithson
image : Simon Terrill, Crowd Theory Thamesmead, 155x250cm, 2017, detail 2
Parallel (of Life and) Architecture – Bath Exhibition
Location: Bath, south west England, UK
University of Bath Buildings
Key University of Bath Architecture
Bath arts complex – ICIA
Design: McInnes Usher McKnight Architects

image courtesy of architects practice
Bath University Arts Complex
University of Bath – Centre for the Arts, Claverton Down campus
Design: Feilden Clegg Bradley Studios

image courtesy of architecture practice
Centre for the Arts at University of Bath
The Edge, arts and management building

image courtesy of architects studio
The Edge at the University of Bath
Bath Architecture
Key Buildings in Bath – selection:
Bath Spa development
Grimshaw Architects
Thermae Bath Spa
Circle Bath – Centre of Clinical Excellence
Foster + Partners
Circle Bath
James Dyson Design School
Wilkinson Eyre
Dyson School of Design Innovation
Bath Architectural Heritage Debate : Speakers incl. Eric Parry + Sir Richard MacCormac
English Architectural Designs
Comments / photos for the New vaulted style of floor cuts concrete usage page welcome